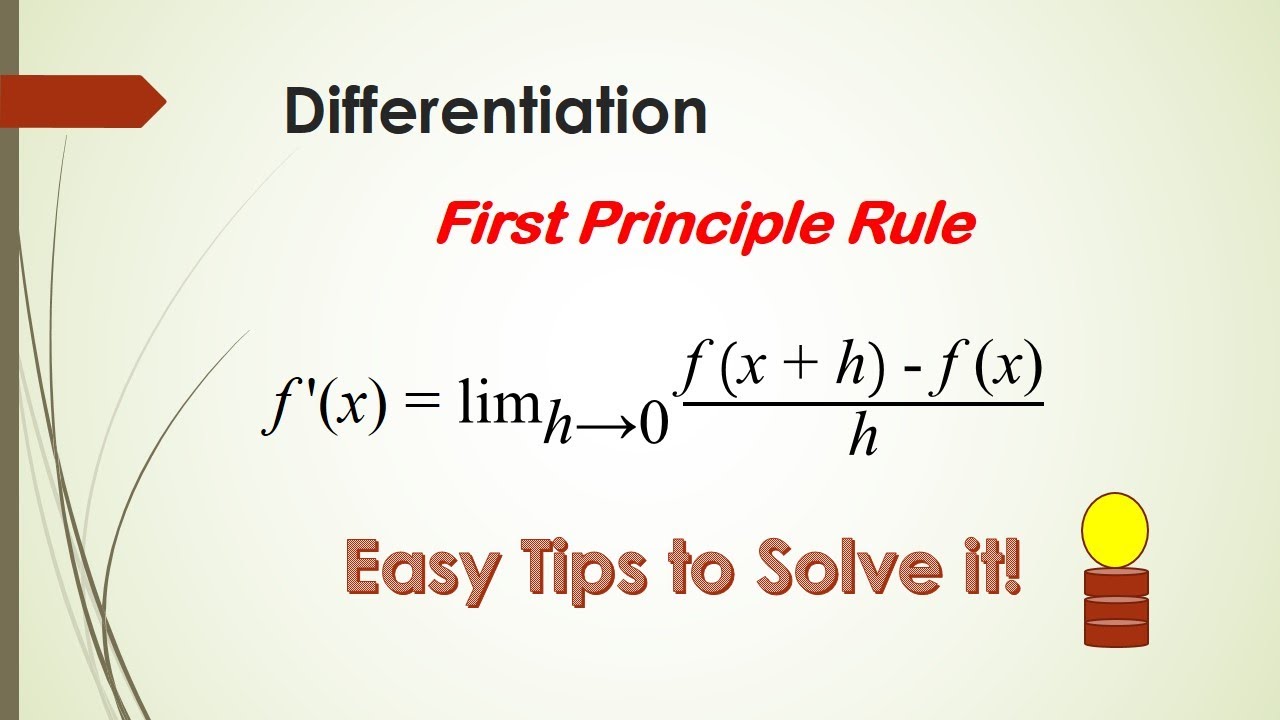
SPM (Add Maths) Differentiation by First Principle Rule YouTube
A Level Maths revision tutorial video.For the full list of videos and more revision resources visit www.mathsgenie.co.uk.
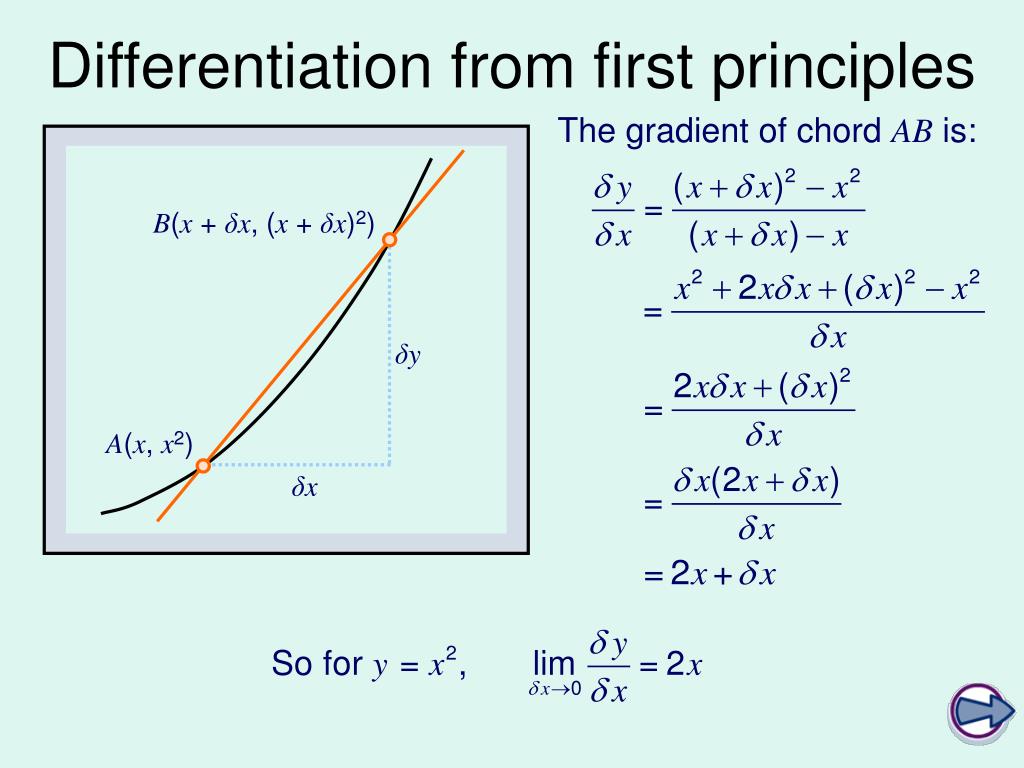
PPT C1 Differentiation from First Principles PowerPoint Presentation ID1806096
Project Team:Daphne Li, Bon Tsang, Cindy Chan, Florence Chan, Leo Fung, Jim Cho, June Hui, Vivian Tsang, Cherry Chin, Esther Ma. Cost Consultant: Northcroft HK Ltd. Client:Architectural Services.

More examples of differentiating from first principles. YouTube
We now have a formula that we can use to differentiate a function by first principles. Let's try it out with an easy example; f (x) = x 2. In this example, I have used the standard notation for differentiation; for the equation y = x 2, we write the derivative as dy/dx or, in this case (using the right hand side of the equation), dx 2 /dx.
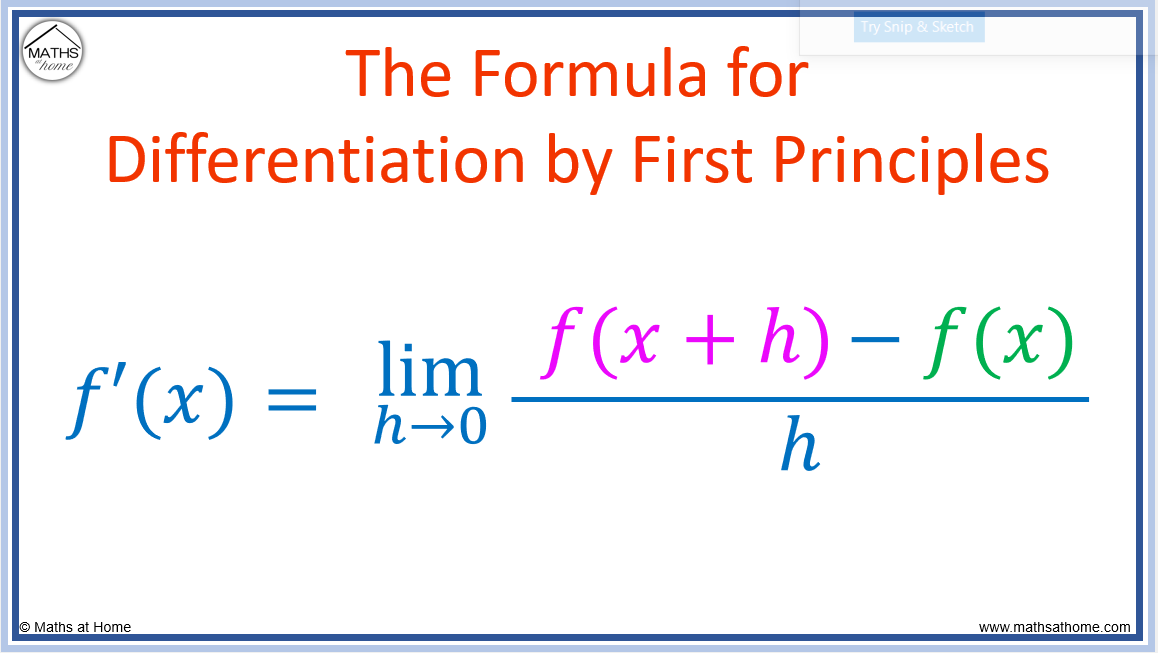
How to Differentiate by First Principles
Worked examples of differentiation from first principles. Let's look at two examples, one easy and one a little more difficult. Differentiate from first principles y = f ( x) = x 3. SOLUTION: Steps. Worked out example. STEP 1: Let y = f ( x) be a function. Pick two points x and x + h. Coordinates are ( x, x 3) and ( x + h, ( x + h) 3).

Example 19 Find derivative from first principle Class 11
The differentiation by first principles formula is f' (x)=limh→0[f (x+h)- (fx)]/h. For any function f (x), find f (x+h) by replacing x with x+h and substitute f (x+h) and f (x) into the formula. Simplify the numerator and divide all terms by h. Finally evaluate the limh→0 by substituting h = 0. The result is the gradient function of f (x).

How to Differentiate by First Principles
STEP 1: Identify the function f (x) and substitute this into the first principles formula. e.g. Show, from first principles, that the derivative of 3x2 is 6x. so. STEP 2: Expand f (x+h) in the numerator. STEP 3: Simplify the numerator, factorise and cancel h with the denominator. STEP 4: Evaluate the remaining expression as h tends to zero.

Differentiation from 1st Principles Calculus by ExamSolutions YouTube
Definition The derivative of a function f(x) f ( x) is denoted by f′(x) f ′ ( x) and is defined as f′(x) = limh→0 f(x + h) − f(x) h, h≠ 0. f ′ ( x) = lim h → 0 f ( x + h) − f ( x) h, h ≠ 0. Using this definition is called differentiating from first principles. The result f′ (x) f ′ ( x), is called the derivative of f(x) f ( x).

Differentiation by First Principle All Formulae of Differentiation YouTube
1 DN1.1: DIFFERENTIATION FROM FIRST PRINCIPLES The process of finding the derivative function using the definition '( x ) = ( x + h f x lim ( ) , h ≠ 0 → 0 is called differentiating from first principles. Examples 1. Differentiate x2 from first principles. f + ′ ( ) x = lim h → 0 = lim h→ 0 = lim h→ 0 = lim h→ 0 = lim h→ 0 = lim h→ 0
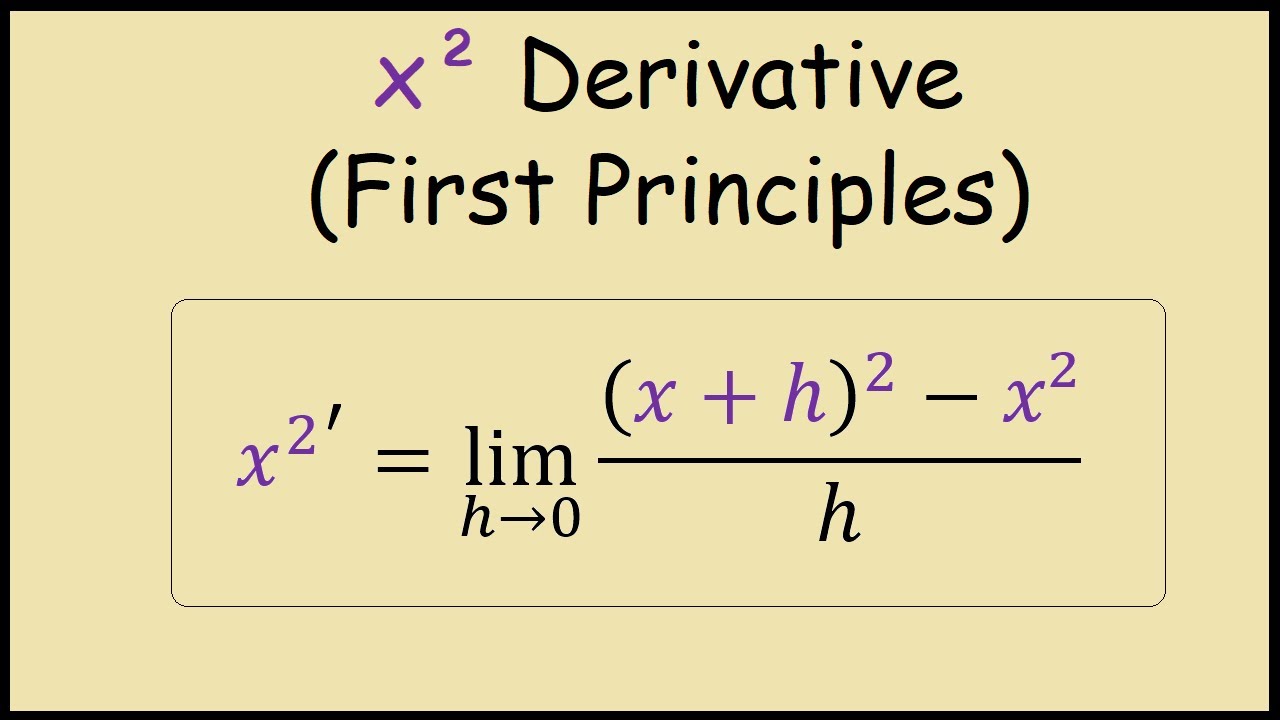
Derivative of x^2 from First Principles YouTube
STEP 1: Identify the function f (x) and substitute this into the first principles formula e.g. Show, from first principles, that the derivative of 3x2 is 6x so STEP 2: Expand f (x+h) in the numerator STEP 3: Simplify the numerator, factorise and cancel h with the denominator STEP 4: Evaluate the remaining expression as h tends to zero
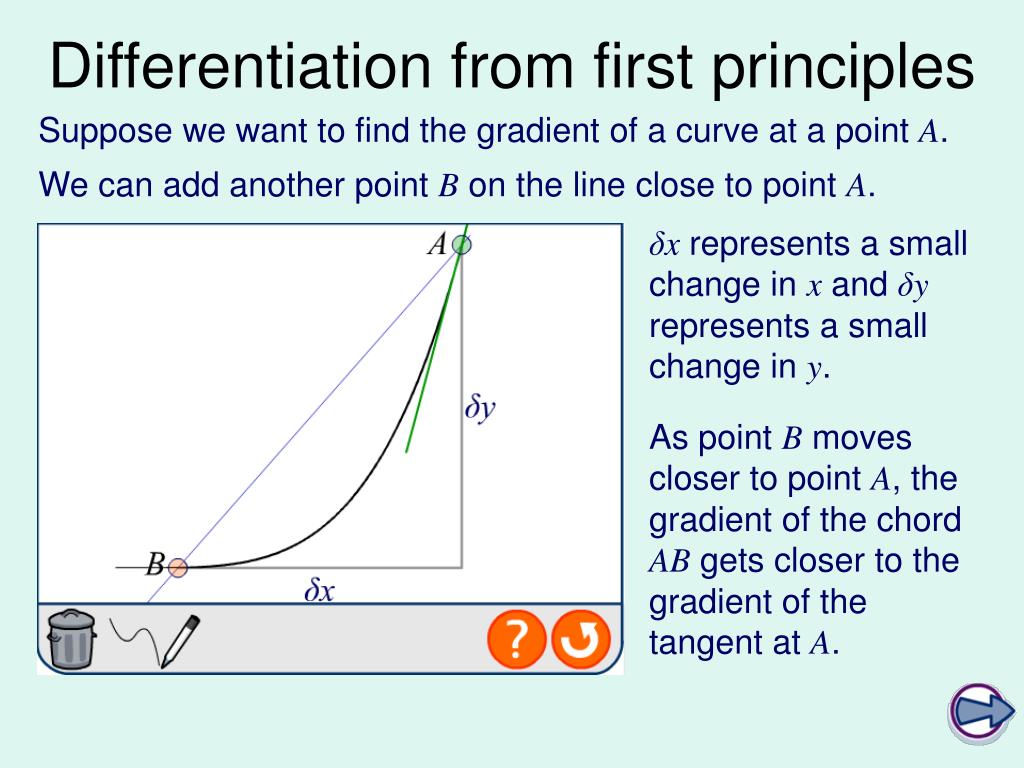
PPT C1 Differentiation from First Principles PowerPoint Presentation ID1806096
In this video we focus on the first Principle of Differentiation, a component of calculus that explains how to determine the derivatives of functions.#learnt.
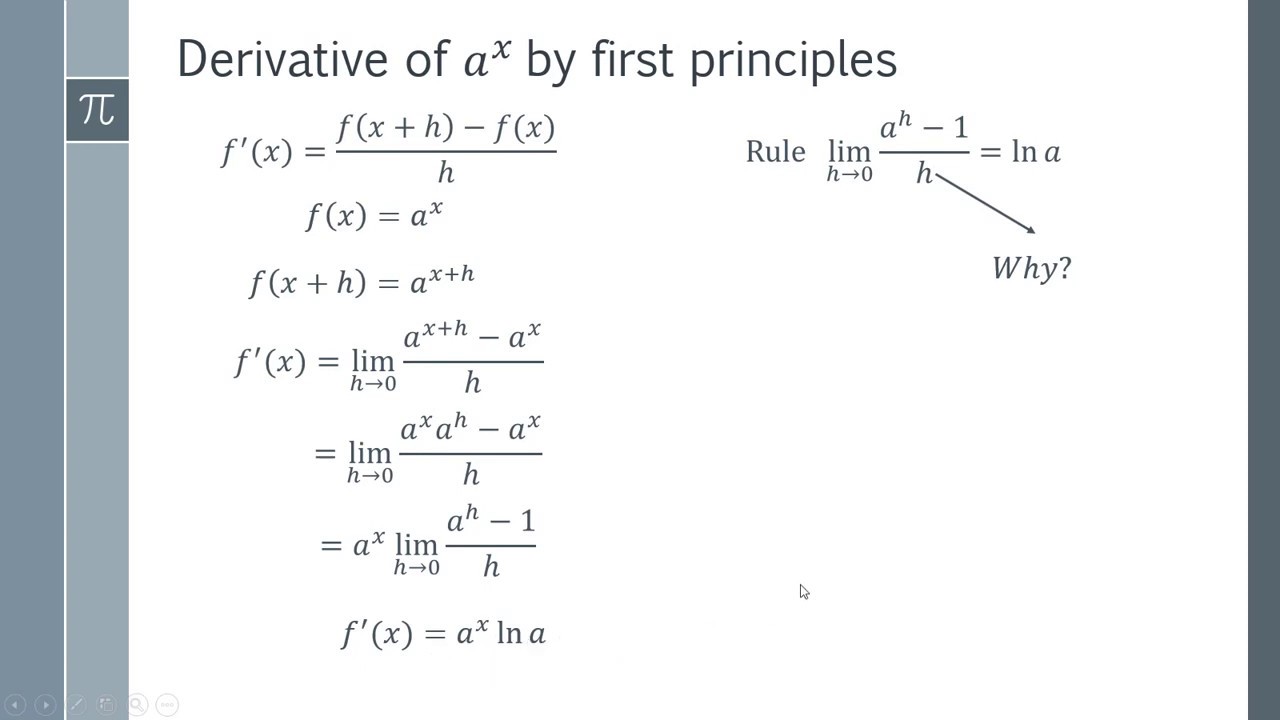
How to Find the Derivative of a^x from First Principles YouTube
Differentiation from First Principles The formal technique for finding the gradient of a tangent is known as Differentiation from First Principles. By taking two points on the curve that lie very closely together, the straight line between them will have approximately the same gradient as the tangent there.

Differentiation from First Principles a simple explanation of how it works YouTube
Definition Let f (x) be a real function in its domain. A function defined such that limx->0[f (x+h)-f (x)]/h if it exists is said to be derivative of the function f (x). This is known as the first principle of the derivative. The first principle of a derivative is also called the Delta Method.
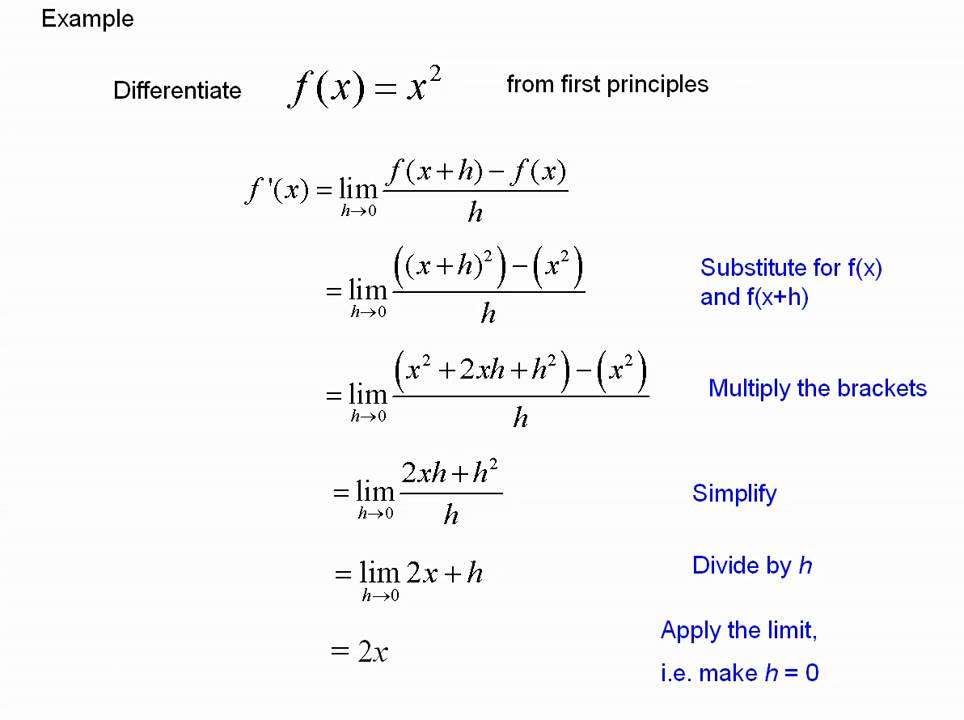
Differentiating from first principles YouTube
Derivative by first principle refers to using algebra to find a general expression for the slope of a curve. It is also known as the delta method. The derivative is a measure of the instantaneous rate of change, which is equal to f' (x) = \lim_ {h \rightarrow 0 } \frac { f (x+h) - f (x) } { h } . f ′(x) = h→0lim hf (x+h)−f (x).

9 Differentiation from first principles YouTube
In this section, we will differentiate a function from "first principles". This means we will start from scratch and use algebra to find a general expression for the slope of a curve, at any value x. First principles is also known as "delta method", since many texts use Δ x (for "change in x) and Δ y (for "change in y ").
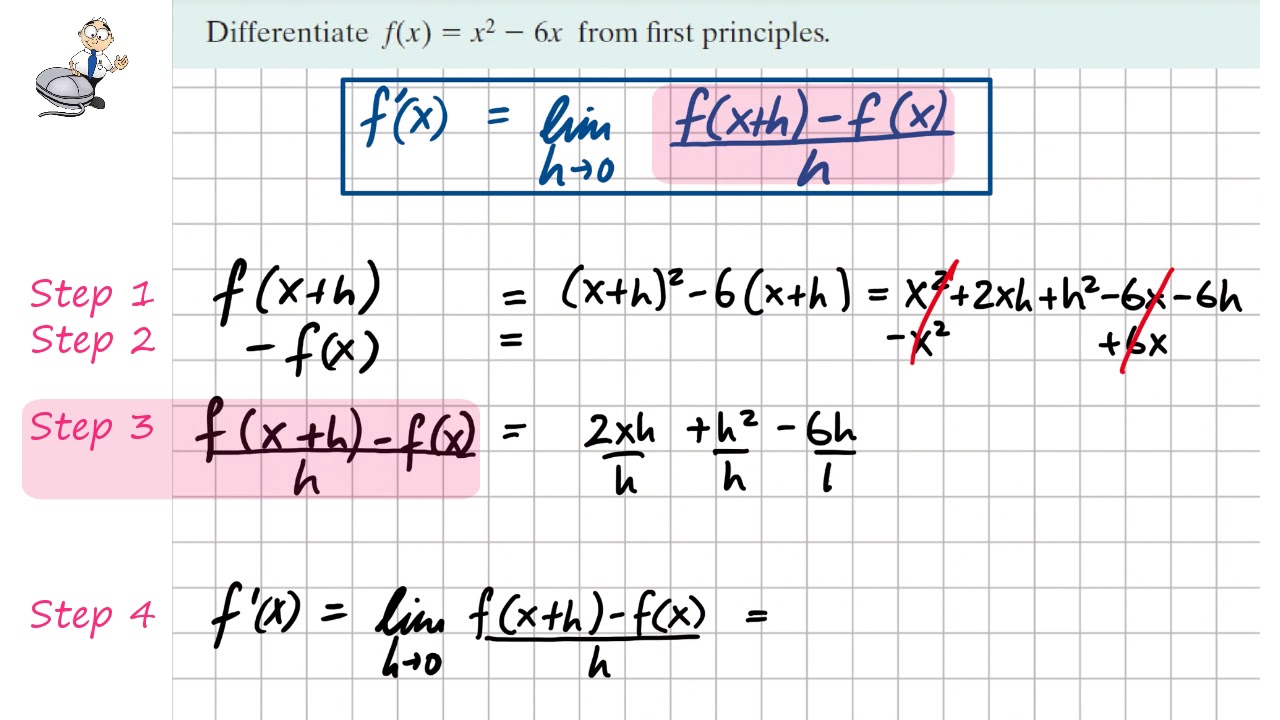
Differentiation 1 eg. 2.2 First principles YouTube
First Principle of Differentiation: Derivative as a Rate Measurer, Geometrical Interpretation of Derivative at a Point A derivative is the first of the two main tools of calculus (the second being the integral). It is the instantaneous rate of change of a function at a point in its domain.

ten Differentiation from first principles YouTube
Differentiation From First Principles This section looks at calculus and differentiation from first principles. Differentiating a linear function A straight line has a constant gradient, or in other words, the rate of change of y with respect to x is a constant. Example Consider the straight line y = 3x + 2 shown below